LAB
EXERCISE 5: Monthly Sales Tax
Goal:
In this exercise, you will learn how to:
1.
Insert the Main Method (Main Entry Point to the Java Program)
2 Import a Java Class Library
3. Declare Variables
4. Declare Constant Variables
5. Create a Constructor (Special Method)
6. Create Methods
7. Create Objects and Call the Methods
Program
Specifications:
A
retail company must file a monthly sales tax report listing the total sales for
the month, and the amount of state and county sales tax collected. The state
sales tax rate is 4% and the county sales tax rate is 2%. The application should calculate and display
the following:
a. The amount of county sales tax
b. The amount of state sales tax
c. The total sales tax (county plus
state)
In the application’s code, represent the county tax rate
(0.02) and the state tax rate (0.04) as constants (Final Variables). Use the constant variables in the calculation
formulas to compute for the taxes.
A. Pre-requisites:
1.
Create a folder on your desktop Exercise-5
2. Launch Eclipse
3. Setup your Eclipse Workspace to point to the Exercise-4
folder
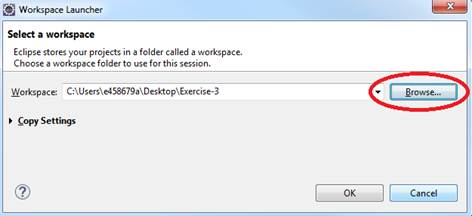
a. Select File-> Switch Workspace
b. Browse and select your Exercie-5 folder as your Workspace.
B. Requirements to setup Java Project:
1. Create
a Java Project and name it as MonthlySalesTax
2. Create
the first Class that will have the Main Method
a.
Name the Class as MainApp
b.
Choose the main method to insert into the
class
![]()
3. Create
the second Class that will have the Constructor and Methods
a.
Name the Class as SalesTax
b.
Do not select the main method stub
![]()
C. Requirements
for the SalesTax Class:
1. Insert
the import java.util.Scanner class
which will allow data to be inputted from the console.
2. Declare
and initialize the Constant variables:
final static double stateTax
= 0.04
final static double countyTax= 0.02
3. Declare
the Class variables- totalSales, taxAmtCounty, taxAmtState
and totalSalesTax
using a double data type
4. Create
the Constructor called SalesTax
a. Declare
the scanner input class objects
b. Prompt
the user to input the data.
c. Assign
the inputted data to the variable
d. Close
the scanner input class object
Below is the code you can copy and paste
|
//
declare the scanner object used to input the total sales from the console //
close the scanner input object |
5. Create
the Method called calcStateTax()
a. This
method should not accept any argument
b. This
method will return a double
c. Insert
the formula taxAmtState = stateTax * totalSales
d. Insert return taxAmtState
6. Create
the Method called calcCountyTax()
a. This
method should not accept any argument
b. This
method will return a double
c. Insert
the formula taxAmtCounty = countyTax * totalSales
d. Insert
return taxAmtCounty
7. Create
the Method called calcTotalSalesTax()
a. This
method should not accept any argument
b. This
method will return a double
c. Insert
the formula totalSalesTax = taxAmtState + taxAmtCounty
d. 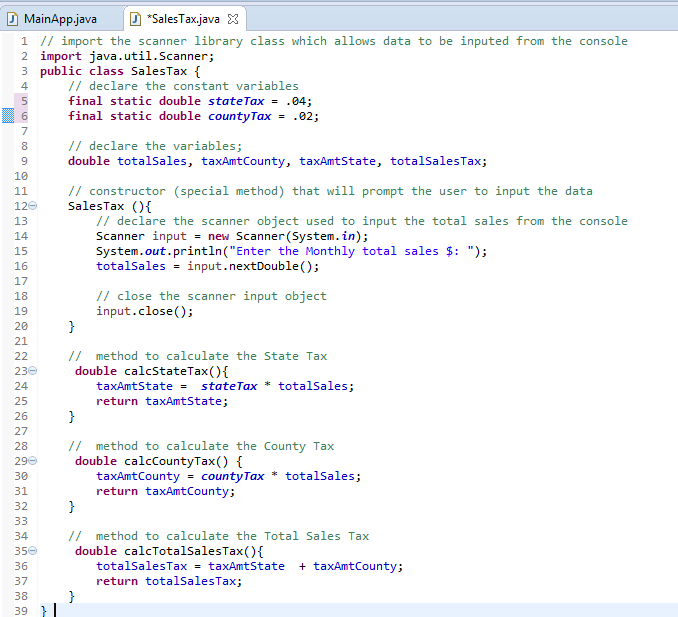 Insert
return totalSalesTax
Insert
return totalSalesTax
D. Requirements for the MainApp Class:
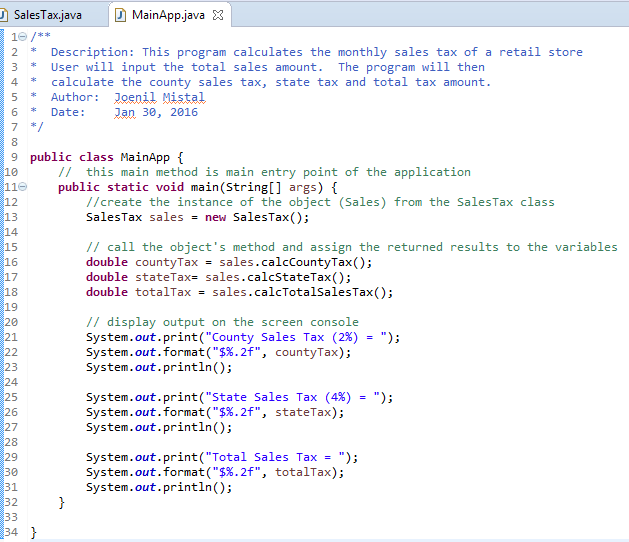
1. Add
comments (documentation)– Program Description, Author and Date
2. Create
the instance of object called sale from the SalesTax class
3. Declare
the countyTax variable as double and assign the return value from
the called object method- sales.calcCountyTax()
4. Declare
the stateTax variable as double and assign the return value from
the called object method- sales.calcStateTax()
5. Declare
the totalTax variable as double and assign the return value from
the called object method- sales.calcTotalSalesTax()
6. Display
the output on the screen console. Below
is the code you can copy and paste
|
//
display output on the screen console System.out.print("State Sales
Tax (4%) = "); |
E. Test:
1. Save your Java code
2. Compile and run your Java program.
3. Verify there is no syntax, logical or run-time
errors.
4. Use the following set of test data to
determine if the application is calculating properly:
Total Sales County Tax State Tax Total Tax
9500 $190 $380 $570
5000 $100 $200 $300
15000 $300 $600 $900
F. Submit your exercise in the Canvas Lab
Exercise #5 Drop Box.
1. Submit the screen shot of the Eclipse
Workbench window showing the Console output screen.
You can use Paint (save as JPG) or Word to paste the screenshot.
2. Zip up and submit the compressed MonthlySalesTax subfolder that is in the Exercise-05
folder.
NOTE: Right click on the subfolder and select Send
to “Compress Folder”. The file will have
a file extension of .zip.